근접 매핑된 리드 기술에 대한 견해
근접 매핑된 리드 기술에 대한 견해
Rady Children's Institute for Genomic Medicine의 Stephen F. Kingsmore 박사는 근접 매핑된 리드 기술에 대한 자신의 견해와 이 기술이 희귀 유전 질환에 대한 신속한 전장 유전체 시퀀싱에 미칠 수 있는 잠재적 영향에 대해 공유합니다.
TruPath Genome을 지원하는 근접 매핑 리드 기술을 사용하여 장거리 정보로 짧은 리드 유전체 시퀀싱 향상

Illumina 시퀀싱은 유전체 매핑 방법의 상당한 발전을 이끌며, 연구자들이 대부분의 인간 유전체에 대해 매우 정확한 커버리지를 달성할 수 있도록 지원해 왔습니다.1 그러나 일부 유전체 영역에서는 참조 유전체에 짧은 리드를 매핑하는 일이 여전히 어렵습니다. 이러한 문제는 주로 반복적이거나 복잡성이 낮은 영역, 높은 시퀀스 상동성을 갖는 영역, 또는 큰 구조적 변이에서 발생합니다.
근접 매핑된 리드 기술은 유전체의 매핑이 어려운 영역에서 개선된 매핑, 유전자 변이의 초장기 페이징, 구조적 변이의 향상된 검출을 가능하게 합니다.

근접 매핑된 리드 기술은 온 플로우 셀 라이브러리 프렙과, 인접한 나노웰의 클러스터에서 얻은 근접성 정보를 통합하는 새로운 인포매틱스를 활용하여 장거리 지노믹 통찰력을 제공합니다. TruPath 유전체 assay에서 제공하는 독창적이고 고도로 단순화된 워크플로우는 원래의 대형 DNA 템플릿과 그에 따른 짧은 시퀀싱 리드 간의 연결을 유지합니다.
TruPath 유전체 assay의 핵심인 근접 매핑된 리드 기술은 종합적인 유전체 분석을 제공하는 고유한 워크플로우를 사용합니다.
플로우 셀 라이브러리 프렙은 가장 간단한 샘플-시퀀서 WGS 워크플로를 생성합니다.
XLEAP-SBS chemistry는 NovaSeq X 시리즈에서 2~16개 런당 샘플 수의 입증된 정확성과 확장성을 제공합니다.
클러스터 근접성 분석으로 탁월한 장거리 유전체 정보 확보
향상된 매핑으로 까다로운 영역을 해결하고 향상된 유전체를 제공
새로운 방법으로 대규모 구조적 재배열 검출 개선
근접 매핑된 리드 기술에서, 표준 또는 고분자량 방법을 사용하여 추출된 DNA를 전이효소가 이식된 플로우 셀에 도입합니다. DNA 절편은 태그멘테이션이라는 프로세스를 통해 나노웰에 포획된 다음 시퀀싱됩니다. 큰 DNA 절편을 포획함으로써 근접 나노웰은 DRAGEN Germline 분석을 통해 새로운 알고리즘을 사용하여 클러스터를 원래 절편에 다시 매핑할 수 있는 constellation과 같은 패턴을 생성합니다. 이는 쇼트 리드 시퀀싱의 입증된 정확성과 장거리 유전체 통찰력을 결합하여 매핑하기 어려운 영역의 매핑을 크게 개선하고 구조적 변이 검출을 향상시키며 초장거리 페이징을 제공합니다.
그림 1a: constellation 패턴의 상면도
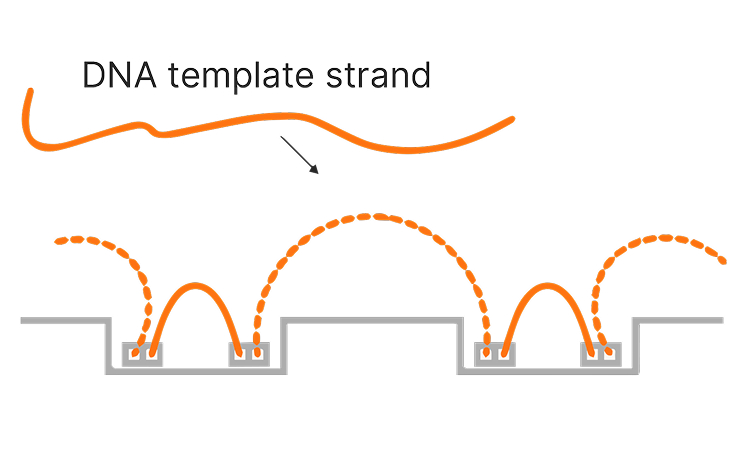
그림 1b: constellation 패턴의 측면도
그림 1: DNA는 플로우 셀에 constellation 패턴으로 부착됩니다. 상면도는 플로우 셀 전체에 걸쳐 분포한 DNA 가닥을 보여주는 타일 일부를 나타냅니다. 측면도는 플로우 셀에서 태그멘테이션을 거치는 템플릿 DNA를 보여줍니다.
근접 매핑된 리드 기술로 구동되는 TruPath 유전체는 향상된 커버리지, 더 높은 정확도의 변이 검출 및 전례 없는 간소함을 통해 인간 생식세포 전장 유전체 시퀀싱 (WGS)을 가능하게 합니다. 플로우 셀 라이브러리 프렙은 시퀀싱 전에 표준 라이브러리 프렙을 생략합니다.
매우 정확하고 포괄적인 인간 생식세포 전장 유전체 시퀀싱.
NovaSeq X 시리즈는 프로덕션 규모에서 데이터 집약적인 애플리케이션을 수행하기 위한 탁월한 처리량과 정확성을 제공합니다.
DRAGEN Germline은 Whole genome, 전체 엑솜 및 표적 패널 NGS 데이터를 위한 정확하고 효율적인(FASTQ~VCF) 2차 분석 솔루션입니다.
근접 매핑된 리드 기술에 대한 견해
Rady Children's Institute for Genomic Medicine의 Stephen F. Kingsmore 박사는 근접 매핑된 리드 기술에 대한 자신의 견해와 이 기술이 희귀 유전 질환에 대한 신속한 전장 유전체 시퀀싱에 미칠 수 있는 잠재적 영향에 대해 공유합니다.
WGS의 미래를 매핑
GeneDx의 랩 혁신팀 이사인 Joseph Devaney 박사는 데이터를 비교하고 근접 매핑된 리드(이전 Constellation) 기술의 잠재적 영향에 대한 자신의 견해를 공유합니다.
매핑된 리드 기술로 분석 수행하기
Illumina의 assay 연구 개발 부문 부담당자인 Louise Fraser 박사가 매핑된 리드 기술(이전의 컨스텔레이션 매핑 판독 기술)이 어떻게 작동하는지, 그리고 수행할 수 있는 분석의 유형에 대해 설명합니다.
Illumina의 Steven Barnard 박사가 혁신적인 멀티오믹스 애플리케이션을 가능하게 하는 최신 Illumina 혁신 기술에 대해 설명합니다. Broad Institute of MIT의 Niall Lennon 박사는 워크플로우, 초기 데이터 및 근접 매핑 리드 기술의 흥미로운 잠재력에 대한 인상을 제공합니다.
근접 매핑된 리드 기술은 현재 NovaSeq X 시리즈에서 사용할 수 있습니다. DRAGEN Germline 2차 분석 파이프라인을 사용하며 분석을 실시하며 Illumina Whole genome 3차 분석 솔루션과 호환됩니다.
근접 매핑된 리드는 근처의 나노웰에 있는 클러스터의 근접 정보와 결합된 표준 쇼트 리드로, 정확한 장거리 지노믹스 통찰력을 생성합니다. 이 워크플로우는 원래의 긴 DNA 템플릿과 그로부터 생성된 짧은 시퀀싱 리드 간의 연결을 유지함으로써 구조적 변이의 향상된 검출, 유전적 변이의 초장거리 페이징 및 유전체의 매핑이 어려운 영역에서의 개선된 해상도를 가능하게 합니다.
아니요, 실험 워크플로우에는 시퀀싱 시스템 변경이 필요하지 않습니다. 이 방법은 새로운 시퀀싱 레시피만 필요하므로 연구원들이 쉽게 접근할 수 있습니다.
롱 리드 시퀀싱은 온전한 긴 DNA 분자의 시퀀싱을 가능하게 합니다. 매핑된 리드 기술 워크플로우는 긴 템플릿 DNA를 패턴화된 플로우 셀에 직접 유도하며, 인접한 나노웰은 동일한 템플릿의 DNA를 포함할 가능성이 높습니다. 대규모 구조적 변이의 검출, 복잡성이 낮은 영역의 매핑, 변이의 초장거리 페이징 등을 포함한 다양한 애플리케이션에서 인포매틱스를 활용해 리드를 높은 신뢰도로 매핑할 수 있습니다.
리드 매핑은 시퀀스 리드로부터 유전체 위치를 결정하는 프로세스를 기술합니다. 정렬은 둘 이상의 시퀀스 사이의 유사성을 식별하는 것을 포함합니다. 예를 들어, 싱글 리드는 유전체 내에서 둘 이상의 위치에 정렬될 수 있지만, 하나의 위치에만 정확하게 매핑됩니다. 리드 매핑 기술은 참조 유전체에 대한 리드 매핑과 정렬 분석을 모두 지원합니다.
Steve Barnard 박사, 매핑된 리드 기술 소개
Illumina의 CTO인 Steve Barnard 박사는 인간 유전체 시퀀싱을 위한 constellation 매핑된 리드 기술을 소개하고, Broad Clinical Labs의 의장 겸 CSO인 Niall Lennon 박사가 합류해 예비 데이터와 통찰력을 공유합니다.

플로우 셀 라이브러리 프렙과 인접 나노웰의 근접성 정보를 통해 어떻게 장거리 지노믹 통찰력을 확보할 수 있는지 알아보세요.
포스터

매핑된 리드의 머신 러닝 및 공동 배치 분석을 사용하여 복잡한 구조적 재배열을 식별합니다.
포스터
전체 인간 유전체에 대한 편향되지 않은 관점을 얻고, 인간의 특성과 질병을 암호화하는 유전적 변이를 평가해 보세요.
유전체학은 희귀 질환의 기저 유전자 변이를 이해하는 데 있어 근본적인 변화를 주도하고 있습니다.
매우 반복적인 영역, 큰 역위 및 전위와 같은 유전체의 복잡한 영역에 대한 심층적인 인사이트를 얻어 보세요.
TruPath Genome을 지원하는 근접 매핑 리드 기술이 어떻게 장거리 유전체 정보와 새로운 인사이트를 얻는 데 도움이 될 수 있는지 알아보세요.
귀하의 이메일 주소는 결코 제3자와 공유되지 않습니다.
참고 문헌