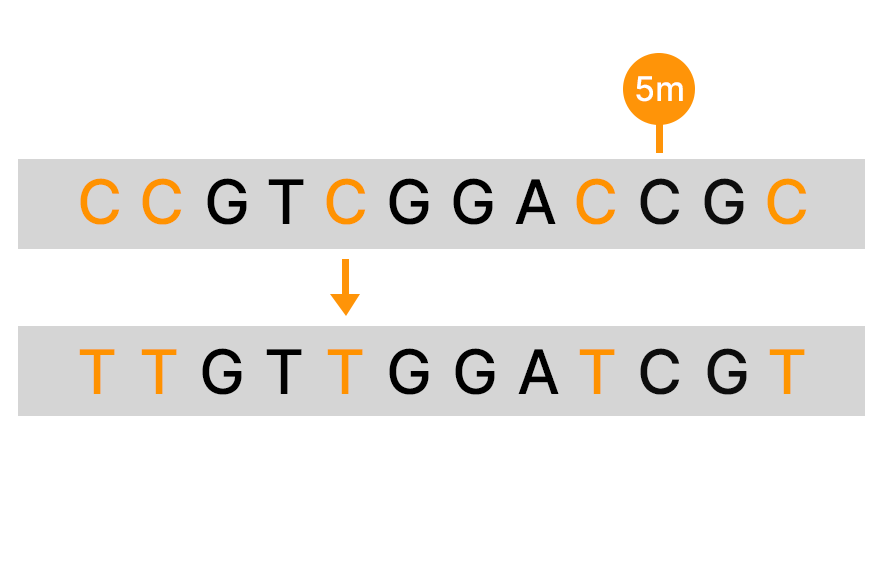
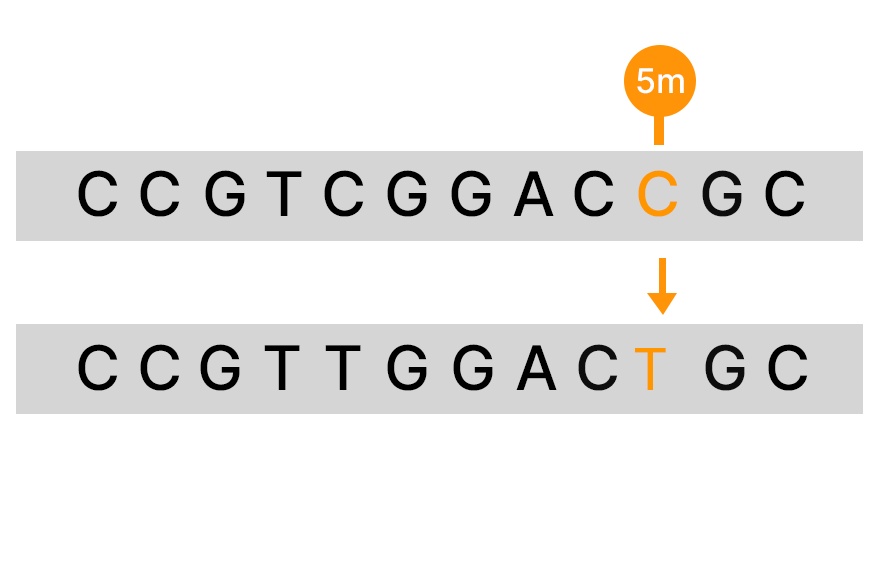
Bisulfite sequencing is a commonly used method for detecting DNA methylation that uses bisulfite to convert unmethylated C to T in sequencing data. However, there are several limitations with this method. It is estimated that approximately 10% of the CpG sites in the genome will be hard to align after bisulfite conversion, and there is DNA degradation that can reach the level of 90%.9
An alternative to bisulfite sequencing, the Illumina 5-base solution, leverages novel chemistry and analyses to enable simultaneous genetic variant and methylation detection. Illumina 5-base chemistry directly converts only 5mC to T in a simple, single-step process that is nondamaging to DNA and retains library complexity. The Illumina 5-base solution can read unmodified bases (A, T, G, C) and 5mC in a single assay.
Learn more about the 5-base solution