Coronavirus Sequencing
How NGS helps fight COVID-19
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) provides an effective, unbiased way to identify new coronavirus strains and other pathogens without prior knowledge of organisms.1 Sequencing was used to identify the novel coronavirus causing COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) early in the outbreak.2 Continued concern over fast spreading, novel variants of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus highlights the need for increased sequencing to detect mutations quickly and prevent the spread of new strains. NGS provides important evidence for public health officials, vaccine and drug developers, and researchers, enabling labs to:
- Track the transmission routes of the virus globally
- Detect mutations quickly to prevent the spread of new strain types
- Identify viral mutations that can affect vaccine potency or avoid detection by established molecular diagnostic assays
- Screen targets for possible COVID-19 therapeutics
- Identify and characterize respiratory co-infections and antimicrobial resistance alleles
Solutions to identify and track novel strains of SARS-CoV-2
Watch how Illumina developed the COVIDSeq Test in record time with the dedication and collaboration of all our employees in the video presentation. Also, learn how the COVIDSeq Assay enables labs to identify and track the emergence and prevalence of novel strains of SARS-CoV-2.
Detect and characterize coronavirus mutations with NGS
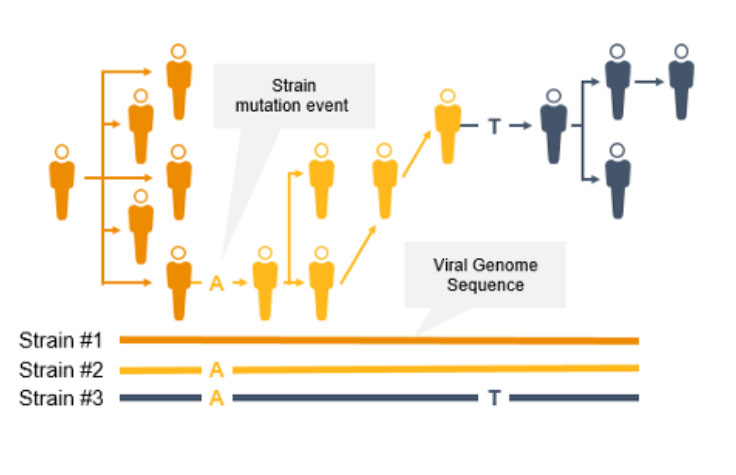
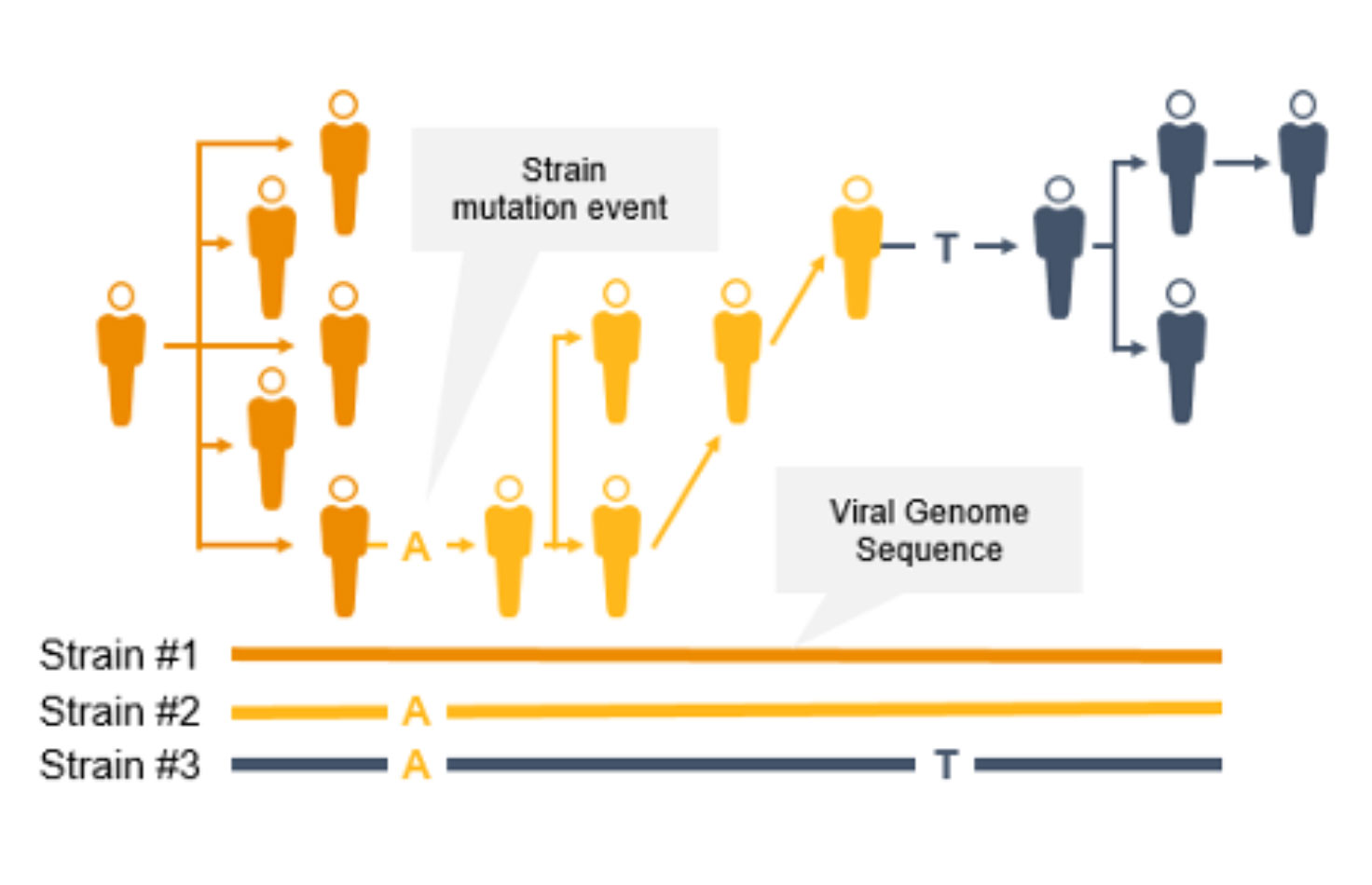
As the coronavirus mutates, new variants can emerge to potentially impact the public. Surveillance and monitoring are critical because mutations can result in greater transmissibility or infectiousness. These coronavirus mutations can make vaccines less effective/protective or even evade test diagnosis.3
NGS is a valuable technology for genomic surveillance of infectious diseases such as COVID-19. Not only can it track the prevalence of coronavirus mutant strains, NGS can also identify novel coronavirus mutations, unlike PCR technology. Using NGS, scientists can detect low-frequency minority variants and multiple polymorphisms as well as novel variants.
Genome-wide strain typing with NGS can help epidemiologists identify and characterize mutations quickly to prevent further spread. Strain-level tracing can support identification of outbreak clusters and transmission routes.
In contrast, PCR is designed to detect specific regions of the pathogen genome; it will not identify new mutations across rapidly evolving pathogen genomes. Furthermore, PCR performance can suffer if mutations occur in the primer or probe binding regions.
Overview of coronavirus sequencing methods
Amplicon sequencing
Detect and characterize SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus by sequencing the whole viral genome. This method involves analyzing the entire genome with ultra-deep sequencing of PCR amplicons.
Hybrid capture sequencing
Detect and characterize coronaviruses, flu viruses, and other pathogenic respiratory tract organisms, as well as associated antimicrobial resistance alleles. These insights can help researchers monitor respiratory infections and optimize infection control strategies. This method captures genomic regions of interest via hybridization to target-specific probes.
Shotgun metagenomics
Comprehensively sequence all organisms in a given sample and identify novel pathogens such as coronaviruses. This NGS method can help accelerate outbreak investigations and support development of new laboratory tests.
Compare coronavirus NGS methods
| Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 | Detection and surveillance of respiratory pathogens | Detect novel virus | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Testing needs | Amplicon | Hybrid capture | Shotgun metagenomics |
| Speed & turnaround time | |||
| Scalable & cost-effective | |||
| Identify novel pathogens | |||
| Track transmission | |||
| Detect mutations | |||
| Identify co-infections & complex disease | |||
| Detect antimicrobial resistance |
Adequately meets laboratory testing needs
Partially meets laboratory testing needs
Amplicon sequencing, hybrid capture, and metagenomics workflows
Frequently Purchased Together
Coronavirus software tools
These tools accelerate coronavirus sequencing data analysis, simplify sample tracking, and facilitate host response studies.
DRAGEN secondary analysis
Access powerful, cutting-edge NGS data analysis tools that support an extensive range of applications, from viral and microbial sequencing to RNA-Seq, whole-genome sequencing, and more.
Correlation Engine
This interactive omics knowledge base and data search engine puts private data into biological context with curated public omics data, and can help researchers investigate factors that regulate the COVID-19 host response.
Clarity LIMS software
This highly customizable laboratory information management system allows labs to track samples and manage workflows efficiently and securely.
COVID-19 NGS webinars
Genomic applications in the fight against SARS-CoV-2
Two leading infectious disease researchers discuss how genomic sequencing technologies are tackling the COVID-19 pandemic.
Clinical metagenomics analysis for SARS-CoV-2
The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the need for tools to detect and monitor emerging pathogens like SARS-CoV-2. NGS led to the initial detection of the coronavirus, and is accelerating test and vaccine development.
NGS for SARS-CoV-2 detection and monitoring
Learn about the broad applicability of NGS for responding to the COVID-19 pandemic, from initial detection and characterization of the novel coronavirus to monitoring, surveillance, and diagnostic detection.
Respiratory virus sequencing application notes
Detect respiratory pathogens & antimicrobial resistance
Rapid hybrid capture sequencing for broad detection of respiratory pathogens (including SARS-CoV-2, flu viruses, and fungi) and associated antimicrobial resistance alleles.
Respiratory Pathogen ID/AMR workflow application noteAnalytical performance of the Respiratory Pathogen ID/AMR workflow application note
Find and characterize respiratory viruses
A rapid hybrid capture sequencing workflow for highly sensitive detection and characterization of coronaviruses, flu viruses, and other respiratory viruses.
Illumina RNA Prep with Enrichment respiratory virus characterization application note
Rapidly detect respiratory viruses
MiniSeq Rapid reagents reduce sequencing run times to < 5 hours, allowing fast detection of coronaviruses and other respiratory viruses.
Fast detection of respiratory viruses with the MiniSeq System application note
Building a state-of-the-art clinical research sequencing lab
Dr. Nir Rainy from the Shamir Genome Center discusses what it takes to build a high-throughput genomics center, how his lab is aiding COVID-19 surveillance efforts in Israel, and his vision for the future of NGS in clinical research.
Read articleCOVID sequencing customer stories
Paving the way with COVID-19 sequencing
A Utah Public Health Lab director discusses how they've expanded their NGS operations in an effort to zero in on SARS-CoV-2 outbreak clusters and establish an infrastructure for future pandemics.
Creating an Australian COVID-19 tracking system
In a groundbreaking initiative, public health labs use Illumina technology to sequence the viral genomes of all positive COVID-19 tests in Australia and track COVID-19 across the country, rather than state by state.
Accelerating COVID-19 host response research
A collaborative environment helps COVID-19 researchers validate hypotheses around important pathways, biomarkers, and potential drug candidate leads.
Improving COVID sequencing in a changing pandemic
How Aegis Sciences moved with the mutations, expanded capacity, and became one of the largest COVID sequencing operations in the world.
Tracking COVID-19 with dust at Ohio State University
A campus lab sequences dust from vacuum bags to understand the variants and viral load of SARS-CoV-2 and other viruses.
Technical tips
Decontaminating Illumina sequencers for novel coronavirus
In keeping with recommendations from the United States CDC and World Health Organization, Illumina recommends this procedure for decontaminating NGS instruments suspected or known to have come in contact with the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV).
Impact of ammonium-based cleaning products on sequencing run performance
Use of ammonia-based cleaners and sanitizing products (frequently utilized to clean labs during the COVID-19 pandemic) in proximity to sequencing run setup can result in decreased sequencing run performance metrics. View tips on how to avoid these issues.
Want to talk to someone about COVID-19 sequencing solutions for your lab?
Contact us today
Related solutions
Tuberculosis surveillance
Learn how genomic-based TB surveillance can support public health officials in detection and transmission of outbreaks.
Antimicrobial resistance surveillance
Get insights into how various NGS methods can offer breakthrough detection capabilities for antimicrobial resistance.
Wastewater sequencing
Learn how wastewater surveillance with NGS is helpful for community-level monitoring of emerging infectious diseases, mutation tracking, and variant trend tracking.
References
- Bulcha B. Review on viral metagenomics and its future perspective in zoonotic and arboviral disease surveillance. J Biol Agr Healthc. 2017; 7(21): 35–41.
- Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382(8): 727–733.
- Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants. who.int/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants. Accessed December 6, 2023.